A conventional truss is a rigid structure composed of geometrically invariable triangular elements. The rods are mainly subjected to axial tension and pressure, and the structural efficiency is very high. For the overhanging and spanning theme of spatial structure, truss structure is almost omnipotent.
Today, starting from the historical development of trusses, we will introduce triangular trusses, beam trusses, hollow trusses, space trusses and other forms, as well as corresponding classic cases.
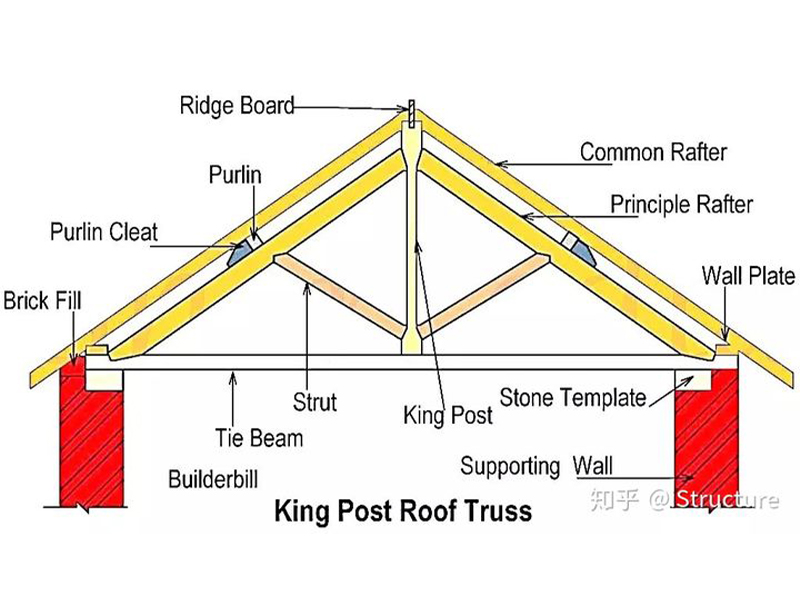
As early as two thousand years ago, human ancestors discovered the stability principle of triangles and invented triangular trusses, which were widely used in wooden roofs of ancient houses. Triangular truss, like beams and arches, is the most important method for ancient buildings to achieve leapfrogging.
The shape of the triangular truss is consistent with the bending moment diagram of the concentrated load in the middle of the simply supported beam. It is more efficient than the beam structure and does not generate thrust on the support like an arch.
Early triangular trusses had only 2 inclined upper chords and 1 horizontal lower chord. Then, based on experience, people tried to add 3 web rods to the position of the middle point of the chord inside the triangle, and evolved into two basic forms of single-post truss (KingPost Truss) and double-post truss (QueenPost Truss).
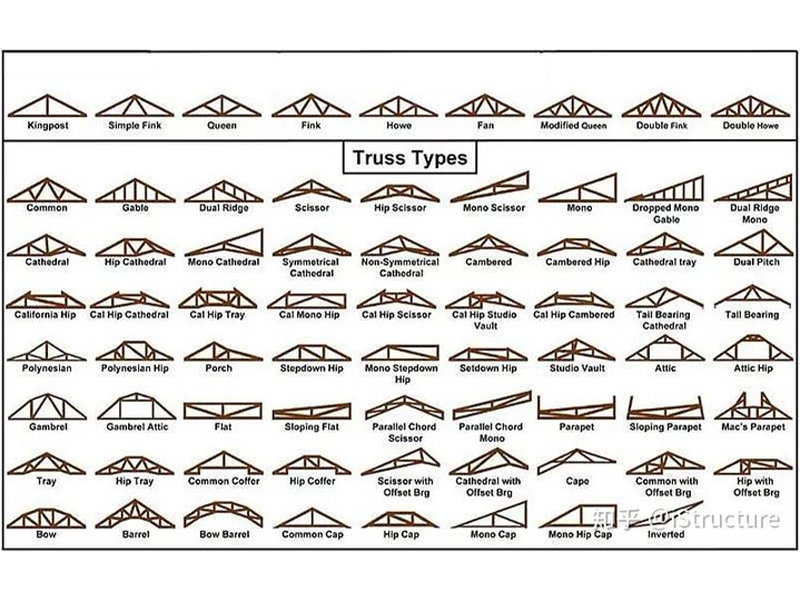
Single-post and double-post roof trusses have not changed much in the long history. Until the middle of the 19th century, various modern truss forms appeared one after another, such as Howe, Fink, Warren, Pratt, etc. The truss material is no longer limited to wood, more and more iron or steel is used.
Among the long-span structures, the earliest existing record is the Moscow Equestrian Gymnasium designed and built by Beta Kru in 1818. The length and width of the building is 160x50m, and the span of the large-span wooden triangular truss is arranged along the short side of 50 meters and the spacing is 5.8 meters. Its span is much longer than the conventional buildings of the same period, and the triangular trusses are embedded with three-layer trapezoidal trusses to resist the huge and uneven snow load.
The upper chord presents a variable cross-section, which conforms to the changing trend of axial pressure. The extra-long lower chord bears a huge tensile force, and is superimposed by two lumbers in two layers. Many connecting members are also arranged between each truss, which are tightly connected by bolts to form a stable whole. The truss design 200 years ago embodies the designer's creativity everywhere.

Beam trusses, also known as parallel chord trusses, are a form that suddenly appeared in the middle of the 19th century. At that time, the western United States was being developed, and the demand for railway bridges was rapidly increasing. Wooden bridges were the mainstream of bridges at that time, and most of them used traditional arch bridge technology from Europe.
The arch bridge has a large bearing capacity under a uniform load, but large deformation occurs under the uneven load of the train. Therefore, wooden bridges generally adopt the combination of arch bridge and reinforced rigid frame. After many times of practice, it has been found that as long as the reinforcing frame is made strong enough, the arch can even be omitted. So all kinds of new trusses appeared one after another, and the era of beam trusses began.

With the study of force balance theory, analytical methods and graphical methods, by the 1880s, engineers had mastered concise and practical truss design methods. At the same time, materials are constantly improving. Engineers used cast iron for compression rods and wrought iron for tension rods, and then replaced them with better-performing steels. More and more large-span truss structures appear, especially in the field of bridges.
The Waibaidu Bridge in Shanghai is China's first all-steel structure riveted bridge. It opened to traffic on January 20, 1908. The bridge is a through-type simply supported steel truss, with two holes spanning 52.12 meters each, and a tram track is laid on the bridge deck.
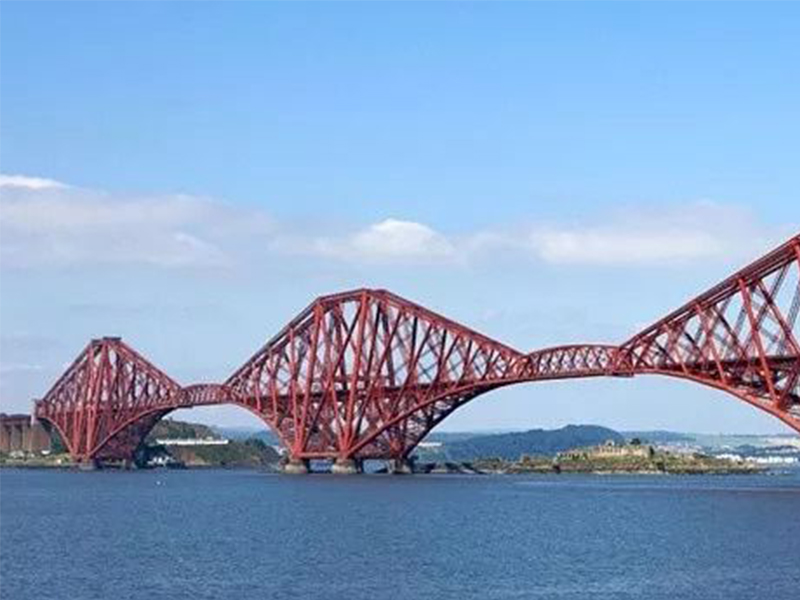

The Forth Bay Railway Bridge built in 1890 is a masterpiece of that era and the second longest multi-span cantilever bridge in the world. The bridge has been built for 130 years, and passenger and freight trains are still used today. It is a milestone in the history of bridge design and construction.
The main span of the bridge is 520m, with a total length of 1620m, which was an unprecedented span at the time. Due to excessive wind, the bridge truss is made to tilt inward.
The bridge has a total of 3 pylons, six outriggers cantilevered 206m in length, which is a statically determinate cantilever truss girder bridge structure. Between the two cantilever trusses of the main span, a 120-long simply supported truss was erected.
The main material of the bridge is steel, which has been eroded by sea breeze and sea water for many years. Corrosion prevention is very important. So much so that there is a saying in the United Kingdom "Paint the Forth Bridge", which describes a job that can never be done.
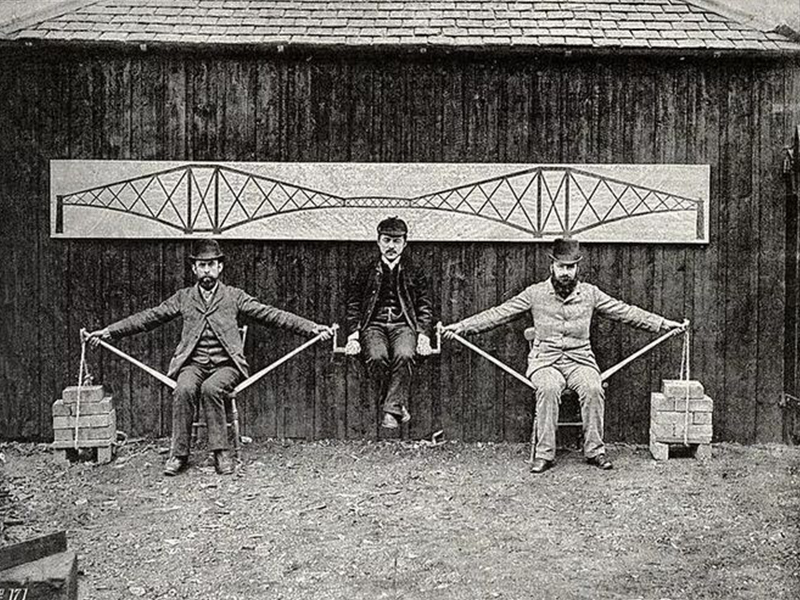
In order to explain the principle of the cantilever truss bridge, the engineers made a simple demonstration test, using the arm as the truss tie rod and the steel rod as the compression rod. part). The three people in the picture are the bridge designer John Fowler, Benjamin Baker, and the engineering director Kayaichi Watanabe.
For a time, the traditional European arch structure also began to be combined with the truss, and the truss system ushered in rapid development.
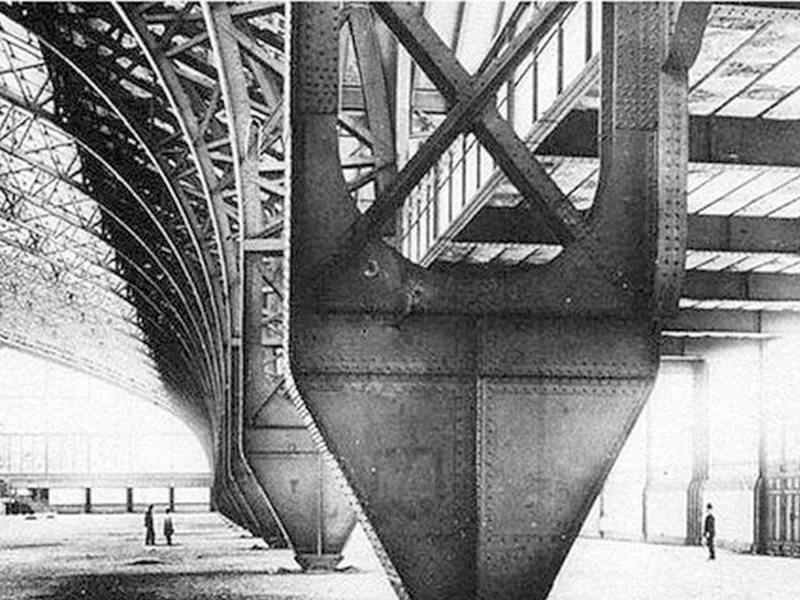
The Paris Expo Machinery Pavilion was designed by engineers J·B.Krantz and Eifel and was completed in 1867. It uses a steel three-hinged arch, and the arch section is in the form of a truss lattice structure. There are a total of 20 such steel arches, forming a huge indoor space with a width of 115 meters and a length of 420 meters.
The steel three-hinged arch has a maximum section height of 3.5 meters and a width of 0.75 meters. These giants become narrower as they approach the ground. They are almost reduced to a point where they meet the ground. Each point has a concentrated pressure of 120 tons, which is a demonstration of technical ability.
Regarding the connection of steel trusses, hinged joints were used in the United States in accordance with the design theory in the early days, and rigid joints were used in Europe due to the use of riveting joints. With the development of welding technology, more and more trusses are connected by welding seams, which makes the truss nodes more concise and dexterous.






 online service
online service +86-592-6095031
+86-592-6095031 manager@yumisteel.com
manager@yumisteel.com Alina_Yuki
Alina_Yuki +8613559086380
+8613559086380 +8615860744964
+8615860744964